The era of commercial spaceflight has officially begun. On May 30, two American astronauts, Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley, climbed into the nose of a Falcon 9 rocket built by Elon Musk’s SpaceX and blasted into orbit. It was the first privately built rocket and capsule ever to put humans into space, restoring America’s ability to launch astronauts from its own soil.
The Speaker argued the launch heralds the beginning of profit-driven human space exploration. “This huge milestone will also catalyze a new space race to ensure America remains the preeminent space power in the face of growing competition from China and Russia,” he said.
In 2017, President Trump reestablished the National Space Council to coordinate national space policy. The Commerce Department revitalized the Office of Space Commerce, which was established over 30 years ago to help enable commercial space activities. The House of Representatives in December approved a $738 billion defense policy bill to create a Space Force, the sixth branch of the US Armed Services.
The global economy is increasingly tied to services provided from space. The Space Force was created in part to protect strategic American space infrastructure, including communications, navigation and spy satellites, from adversaries such as China and Russia.
Government activity in space is growing, but over 80 percent of the $415 billion space economy is commercial. Current industry projections place the 2040 global space economy at between $1 and $3 trillion. This includes activities such as space tourism, space-based mining and manufacturing, and space colonization. “The future of space is going to be commercial in nature, not dominated by government agencies and their priorities,” the Speaker said. Besides resource-rich asteroids, scientists infer the lunar surface could include thorium, magnesium, platinum, titanium, silicon, water, aluminum, and iron ore.
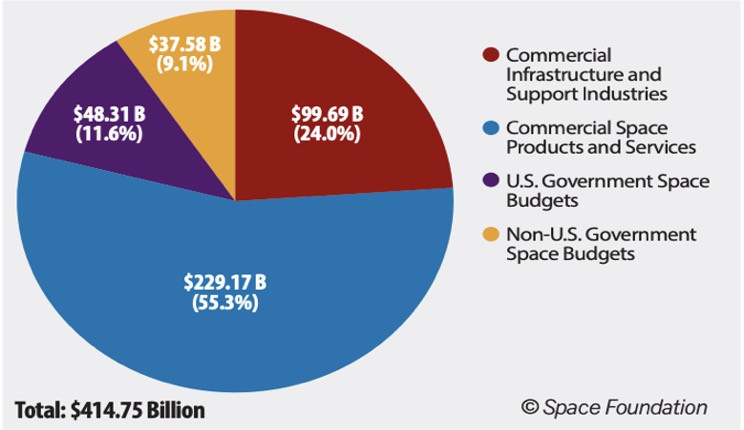
Source: Space Foundation
China’s “space dream” is to “explore the vast universe, develop aerospace enterprises, and build a strong aerospace country.” By 2045, China aims to be the leading space power, setting the stage for the 100th year celebration of the establishment of the People’s Republic. Chinese space scientists are working on plans to capture a Near Earth Asteroid and bring it to Earth to inspect and extract its resources.
Today, growth in the commercial space industry is driven primarily by venture capital. In the past 10 years, more than $25.7 billion was invested in 535 space companies globally. In 2019 alone, $5.8 billion was invested—the largest investment year on record. About 43 percent of the capital went to companies outside America. Over 70 countries now have meaningful space activities. SpaceX has come to dominate the industry and is valued at close to $40 billion.
The Speaker commented that there are no great proxies to play the space theme in the public markets.

Photo: Space X